Edible oils, including vegetable oils and animal fats, are among the most important foods for humans and therefore require the highest quality. The quality of the final oil product not only depends on the quality of the raw oil, but also is closely related to the refining method. Centrifugal separators play an integral role in the refining process. In the edible oil refining process, including degumming and neutralization, when the production capacity exceeds 30Tons/day, there is no doubt that the disc separator is the best choice. However, when the production capacity is less than 20Tons/day, high-speed tubular bowl centrifuges are still used by a large number of oil refineries. In addition to its low purchase and maintenance costs, it is also inseparable from its excellent separation effect.
Edible oils and fats neutralization and degumming with tubular bowl centrifuge
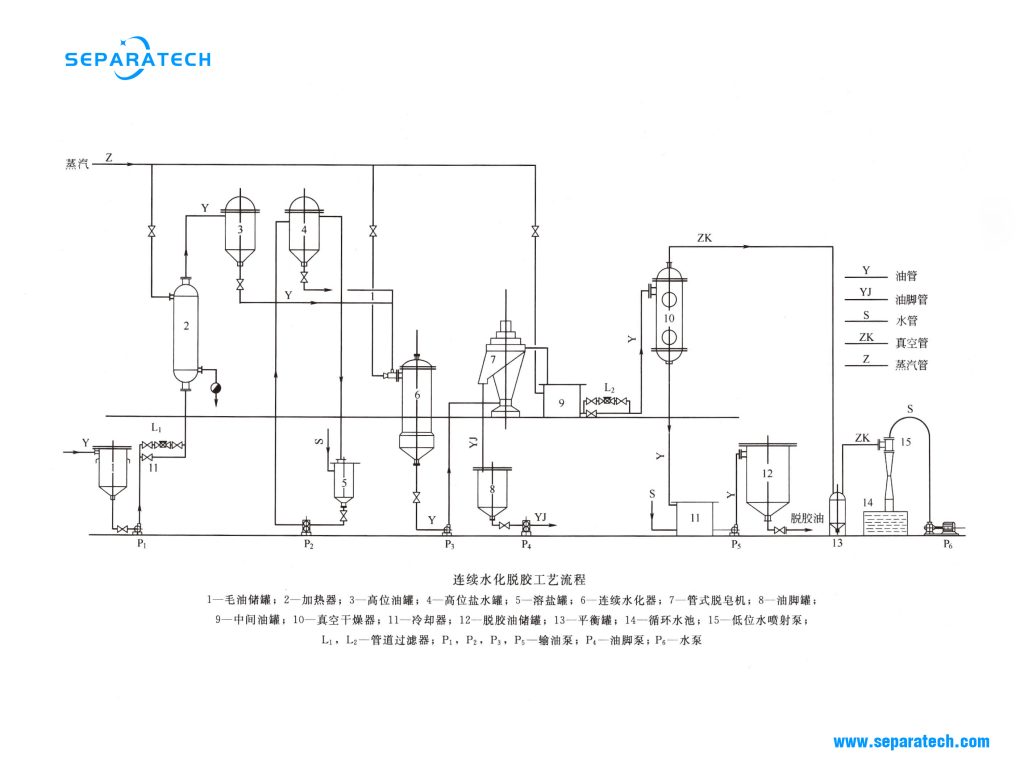
1-Crude oil storage tank
2-Heater
3-High level oil tank
4-High level brine tank
5-Salt tank
6-Continuous hydrator
7-Tubular centrifuge
8-Oil foot tank
9-Intermediate oil tank
10-Vacuum dryer
11-Cooler
12-Degumming oil storage tank
13-Balance tank
14-Circulating pool
15-Low level water jet pump;
L1, L2-pipe filter
P1, P2, P3, P5 – Oil transfer pump
P4 -Oil foot pump
P6-Water pump
Degumming
Degumming is the initial step in the refining process of crude vegetable oils, particularly those extracted from oilseeds like soybean, rapeseed, sunflower, and palm. The primary objective of degumming is to remove phospholipids, also known as gums, from the crude oil. These phospholipids, including phosphatides such as phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylinositol, are undesirable components that can cause refining difficulties and reduce the quality and stability of the oil.
Degumming typically involves treating the crude oil with water, which hydrates the phospholipids, causing them to form complexes that can be separated from the oil. Various methods are employed for degumming, including water degumming, acid degumming, and enzymatic degumming. Each method has its advantages and is selected based on factors such as oil type, processing efficiency, and desired end-product characteristics.
Neutralization
Neutralization, also known as alkali refining or deacidification, is a crucial step in edible oil refining aimed at removing free fatty acids (FFAs) and other acidic impurities from the crude oil. FFAs are formed during the oil extraction process or through hydrolysis of triglycerides in the presence of water, leading to undesirable flavors, odors, and reduced stability in the oil.
Neutralization involves the addition of an alkaline solution, commonly sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), to the crude oil. The alkaline solution reacts with the FFAs and other acidic impurities to form soapstock, which can be separated from the oil through centrifugation or other mechanical means. This process effectively reduces the acidity of the oil, improves its flavor and odor profile, and enhances its stability during storage and high-temperature processing.
Tubular bowl centrifuge
The high-speed tubular bowl centrifuge is a typical oil / soapstock separation centrifuge. It is composed of five parts: a high-speed pulley (a small pulley), a transmission pulley (a large pulley), a pressure pulley, a centrifugal bowl, and a feeding injection component. These five parts are connected by the frame, transmission belt and hanging shaft to form a centrifuge as a whole.
The nominal capacity of the machine is 10 tons/24 hours; the power is 2.2kw.
The rotation speed of the tubular bowl centrifuge is 15,000 to 16,000 revolutions per minute. The centrifugal force field generated by the rotating bowl during operation is 13,200 times greater than the gravity field. This powerful centrifugal force field causes the oil and soapstock entering the high-speed rotating centrifugal bowl to generate different centrifugal forces. As the three equally divided rotary blades in the bowl rotate at high speed, the soapstock gathers on the outer layer and the oil is in the middle. When going up from the bottom of the bowl, the oil and soapstock gradually separated, and the oil flows from the middle outlet along the The layered cap flows into the oil outlet from where leave the centrifuge. The soapstock passes through the gravity ring (commonly known as the neck ring) from the outlet of the bowl wall, and is thrown into the outlet of the casing through the gland cover and discharged, thereby achieving oil and soap separation.
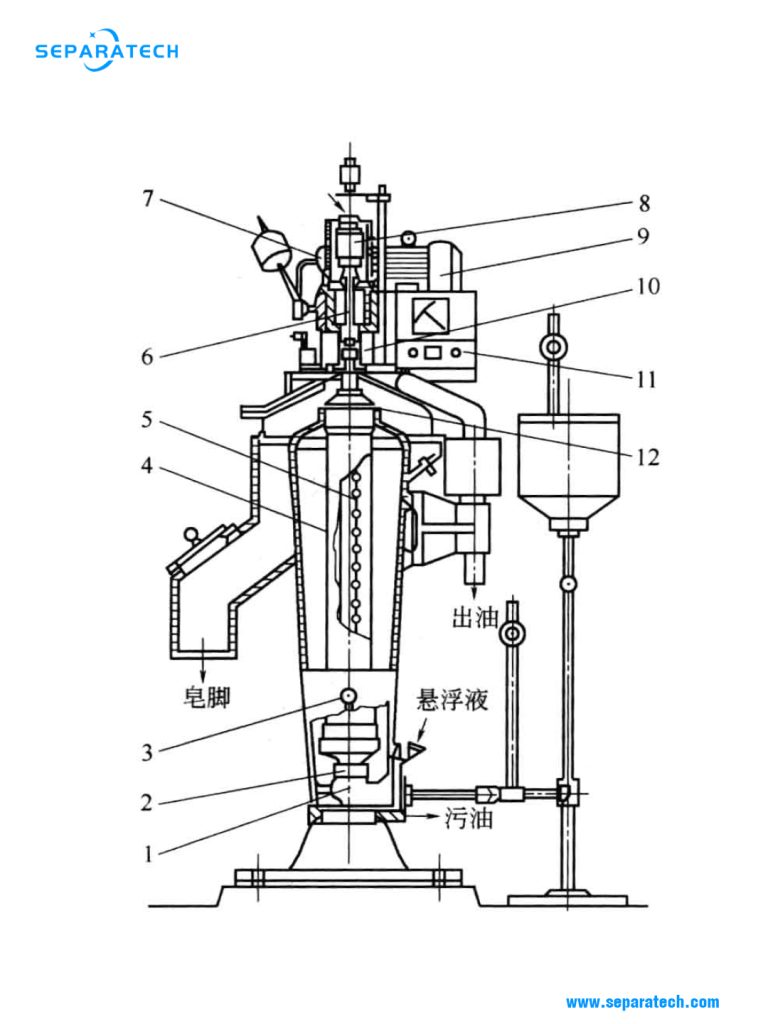
1-Injector; 2-Guide bearing; 3-Brake; 4-Bowl; 5-Divider; 6-Flexible shaft; 7-Pressure pulley; 8-Transmission wheel; 9-Motor; 10-Connecting nut; 11-Switchboard; 12-Dividing ring;
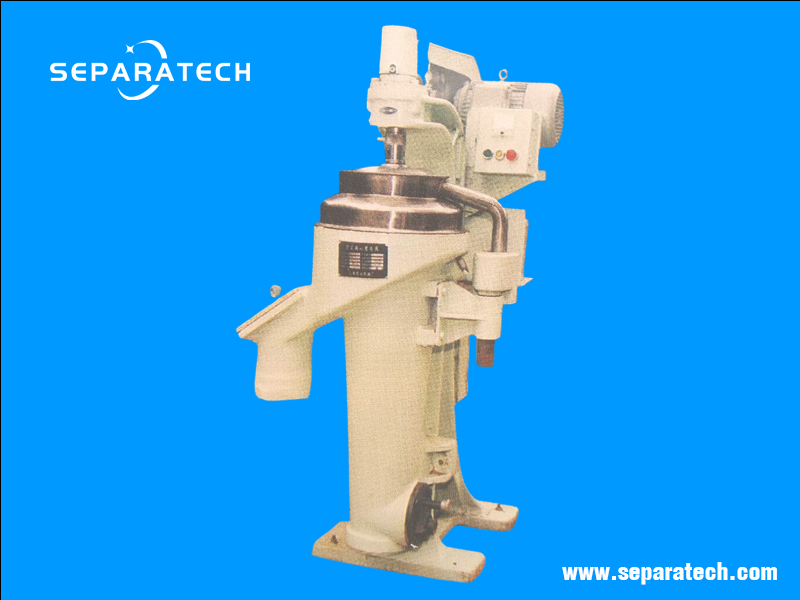
Technical parameters
Designation: GFZ105
Capacity: 10Ton/day
Bowl ID: 105 mm
Bowl length: 753 mm
Bowl speed: 15000 rpm
G-force: 13000 g
Motor: 4 Kw
Weight: 450 Kg
If you are looking for tubular bowl centrifuge for edible oils and fats neutralization and degumming, look no further than SEPARATECH. Contact us today to get a free quote and consultation. We will help you find the best solution for your separation and refining needs.